An inactive screen is a great way to conserve battery life. But what if you need your device’s display to stay on for an extended period? Whether you’re following a recipe, presenting on a projector, or simply want to keep an eye on something, there are ways to prevent your screen from automatically turning off. Here, we’ll explore methods for various devices, along with some considerations to keep in mind.
Understanding Screen Timeouts
Most devices have a built-in screen timeout feature. This setting determines how long the screen remains active after the last user interaction before automatically going dark. Timeouts are set to optimize battery life by turning off the display, a major power consumer, when not in use.
Adjusting Screen Timeout Settings
The process for adjusting screen timeout settings varies depending on your device’s operating system. Here’s a general breakdown for common devices:
-
Smartphones (Android):
- Navigate to your device’s Settings app.
- Locate the “Display” or “Screen” section.
- Look for a setting labeled “Screen timeout,” “Auto-lock,” or similar.
- Select your desired timeout duration, including options like “Never” if available.
-
Smartphones (iOS):
- Open the Settings app on your iPhone or iPad.
- Go to “Display & Brightness.”
- Under “Auto-Lock,” choose your preferred timeout duration, with “Never” being an option on some models.
-
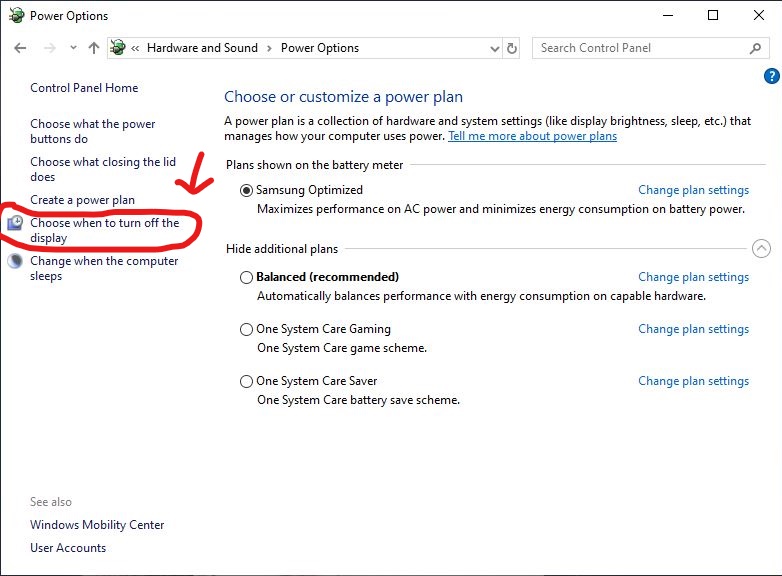
Computers (Windows):
- Open the Control Panel.
- Go to “Hardware and Sound” then “Power Options.”
- Select your current power plan and click “Change plan settings.”
- Click “Change advanced power settings.”
- Expand “Display” and then “Turn off display after.”
- Set the desired timeout values for “On battery” and “Plugged in.”
-
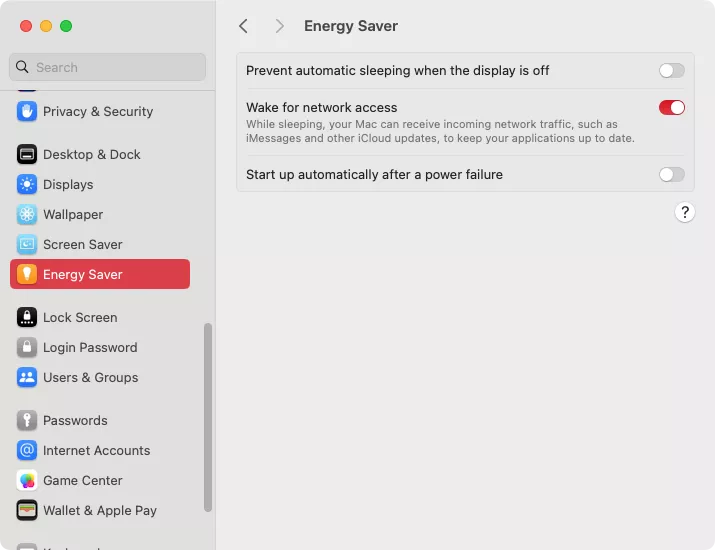
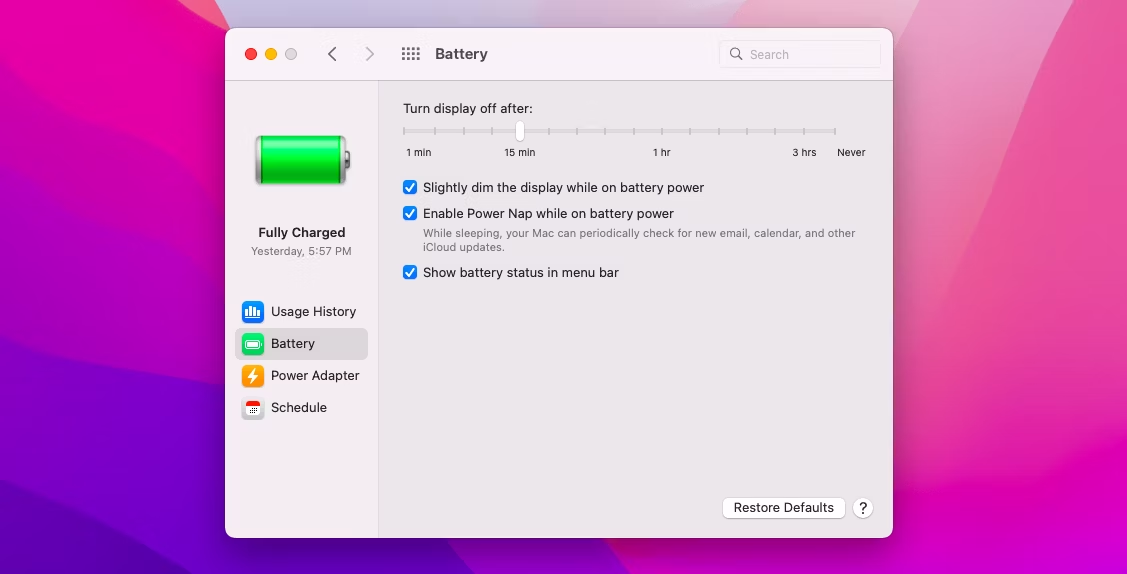
Computers (macOS):
- Click the Apple menu and select “System Preferences.”
- Go to “Battery” or “Energy Saver” depending on your macOS version.
- Adjust the slider for “Turn off display after” to your preferred duration.
Alternative Methods for Keeping the Screen On
For some devices or situations, adjusting timeout settings might not be ideal. Here are alternative approaches:
-
Video Playback: Playing a video on most devices will prevent the screen from turning off as long as playback continues. This can be a handy trick if you need the display active for a short period.
-
Presentation Mode: Many laptops and tablets offer a presentation mode that keeps the screen on while connected to an external display. This is particularly useful for presentations or lectures.
-
Third-Party Apps (Android): The Google Play Store offers apps like “Caffeine” that can prevent the screen from turning off indefinitely. However, use these apps with caution as they can significantly impact battery life.
Things to Consider
While keeping the screen on can be useful in certain situations, there are some drawbacks to be aware of:
-
Battery Drain: The display is a major power consumer. Disabling timeouts will significantly reduce your device’s battery life.
-
Screen Burn-In: On OLED screens, prolonged static images can cause permanent burn-in, a ghost image faintly visible on the display. Take breaks and avoid keeping the screen on for extended periods with static content.
-
Accidental Touches: With the screen constantly active, accidental touches are more likely. This could lead to unintended actions or unwanted screen changes.
Close or disable any unnecessary apps running in the background
Absolutely, closing or disabling unnecessary background apps can be a great way to improve your device’s performance and potentially extend battery life. Here’s how to tackle background apps on different operating systems:
Android:
-
Identify the Culprits: Head to Settings > Apps. Here, you can see a list of all installed apps. Look for apps you rarely use or suspect might be draining battery.
-
Force Stop or Disable: Tap on the chosen app. You’ll see options like “Force Stop” which shuts down the app entirely, or “Battery” where you might find a toggle to disable background activity. “Force Stop” is ideal if you don’t plan to use the app soon, while disabling background activity allows the app to function normally when you open it, but restricts its ability to run silently in the background.
iOS:
- App Offloading: Unlike Android, iOS doesn’t offer a direct way to disable background app refresh. However, you can offload unused apps. Go to Settings > General > iPhone Storage. Here, you’ll see a list of apps and their storage usage. Tap on an app you rarely use. If the option “Offload App” appears, select it. This frees up storage space and prevents the app from running in the background, while keeping your app data intact for when you reinstall it later.
Windows:
-
Task Manager: Press Ctrl+Shift+Esc to open Task Manager. This displays all running processes and their resource usage. Look for apps with high CPU or memory usage that you suspect might be unnecessary. Right-click the app and select “End task” to close it.
-
Startup Apps: Some apps set themselves to launch automatically when you start your computer. This can slow down boot time and consume resources. Open Task Manager and go to the “Startup” tab. Here, you can see a list of apps configured to run at startup. Right-click on unnecessary apps and select “Disable” to prevent them from auto-starting.
General Tips:
- Review App Permissions: When installing apps, be mindful of the permissions you grant them. Restricting access to features like location services when not needed can help reduce background activity.
- Battery Optimization: Most devices offer battery optimization features. Utilize these to limit background activity for specific apps or let the system manage them automatically.
By following these steps and keeping an eye on background apps, you can streamline your device’s performance and potentially extend battery life.
Making an Informed Choice
The best approach to keeping your screen on depends on your specific needs and device capabilities. If you only need the screen active for a short while, adjusting the timeout settings is a good option. For longer durations, consider alternative methods like video playback or presentation mode, keeping in mind the potential impact on battery life and screen burn-in. Third-party apps can be a last resort, but use them judiciously to avoid excessive battery drain.
Ultimately, the goal is to strike a balance between keeping the screen on when needed and conserving battery life when not in use. By understanding the options available and considering the trade-offs, you can ensure your device’s screen stays lit when it matters most.


