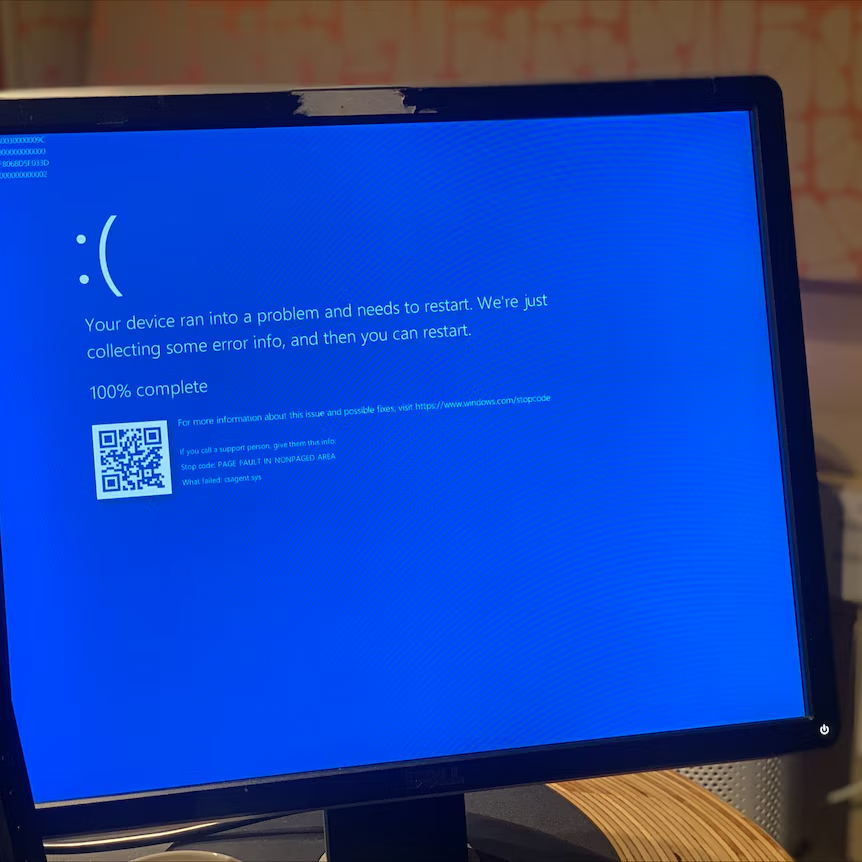
The Blue Screen of Death (BSOD), a dreaded sight for any Windows user, is a critical system error that halts the computer’s operation. It’s a visual indicator of a severe hardware or software problem. While the BSOD was more common in earlier versions of Windows, it can still occur in Windows 11, though less frequently due to improved system stability.
Common Causes of BSOD in Windows 11
Several factors can trigger a BSOD in Windows 11. Here are some of the most common causes:
- Hardware Issues:
- Faulty Hardware: Defective components like RAM, CPU, GPU, or storage devices can lead to BSODs.
- Overheating: Excessive heat can cause components to malfunction and trigger system crashes.
- Loose Connections: Improperly connected cables or devices can disrupt system stability.
- Driver Problems: Outdated, incompatible, or corrupted drivers can cause conflicts and lead to BSODs.
- Software Conflicts: Incompatible or malfunctioning software applications can interfere with the operating system and trigger errors.
- Malware and Viruses: Malicious software can damage system files and cause BSODs.
- System File Corruption: Corrupted system files can destabilize the operating system and result in errors.
- Hardware Overclocking: Pushing hardware beyond its intended limits can increase the risk of instability and BSODs.
Identifying the Cause of a BSOD
When you encounter a BSOD, Windows typically displays a Stop Code, which provides a clue about the underlying issue. You can use online resources or consult technical support to interpret the Stop Code and narrow down the potential causes.
Troubleshooting Steps for BSODs
If you’re facing recurring BSODs, here are some troubleshooting steps you can follow:
- Check for Hardware Issues:
- Inspect for physical damage to components.
- Ensure proper cooling and ventilation.
- Reseat any loose cables or devices.
- Test components individually if possible.
- Update Drivers:
- Visit the manufacturer’s website to download the latest drivers for your hardware.
- Install the drivers carefully, following the provided instructions.
- Scan for Malware:
- Use a reputable antivirus software to scan your system for malware.
- Remove any detected threats.
- Check for Software Conflicts:
- Temporarily disable non-essential applications and see if the BSODs stop.
- If you identify a conflicting application, try updating it or uninstalling it.
- Verify System File Integrity:
- Use the System File Checker (SFC) tool to scan and repair corrupted system files.
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator and type
sfc /scannow.
- Disable Overclocking (if applicable):
- If you’ve overclocked your hardware, revert to default settings.
- Check Event Viewer:
- Examine the Event Viewer for any error messages related to the BSODs.
- This can provide additional clues about the cause.
- Create a System Restore Point:
- Before making significant changes, create a system restore point so you can revert to a previous state if necessary.
Preventing Future BSODs
To minimize the risk of future BSODs, consider the following preventive measures:
- Keep Software Up-to-Date: Install the latest updates for Windows and your applications.
- Monitor System Health: Use tools to monitor system temperature, CPU usage, and other vital statistics.
- Back Up Your Data Regularly: Create regular backups of your important files to protect them in case of a system crash.
- Avoid Overclocking (if possible): Overclocking can increase the risk of instability.
- Use a Stable Power Supply: A reliable power supply can help prevent system crashes.
Regular system maintenance
Regular system maintenance is essential for keeping your computer running efficiently and preventing performance issues. By following a few simple steps, you can ensure that your system remains optimized and free from errors.
Key Areas of System Maintenance
-
Software Updates:
- Operating System: Keep your operating system (Windows, macOS, Linux) updated with the latest patches and security fixes.
- Applications: Regularly update your software applications to address bugs, improve performance, and enhance security.
- Drivers: Ensure your device drivers are up-to-date to avoid compatibility issues and optimize hardware performance.
-
Malware Scanning:
- Regular Scans: Use reliable antivirus software to scan your system for malware and viruses on a regular basis.
- Real-time Protection: Enable real-time protection to monitor your system for potential threats and intercept them before they can cause harm.
-
Disk Cleanup:
- Remove Junk Files: Use your operating system’s built-in disk cleanup tool to remove temporary files, old downloads, and other unnecessary data that can clutter your storage.
- Optimize Disk Space: Regularly check your disk space usage and delete any large files or programs that you no longer need.
-
Defragmentation:
- Organize Files: Defragment your hard drive to improve file access times and overall system performance. This is especially important for traditional hard drives.
- Check for Optimization: Many modern operating systems automatically defragment SSDs, so you may not need to do it manually.
-
Registry Cleaning (Optional):
- Clean Up Registry Entries: While registry cleaning tools can help remove invalid or unused registry entries, use them with caution and only from reputable sources. Excessive registry cleaning can sometimes cause instability.
-
Hardware Maintenance:
- Clean Hardware: Keep your computer’s hardware clean by removing dust from fans, vents, and internal components.
- Check Connections: Ensure that all cables and connections are secure to prevent hardware malfunctions.
- Monitor Temperature: Use monitoring tools to keep an eye on your system’s temperature and prevent overheating.
Additional Tips
- If you’re unable to resolve the BSOD issue on your own, consider seeking professional technical assistance.
- Be cautious when installing third-party software, as some applications can be incompatible or poorly coded.
- If you’re frequently encountering BSODs, it may be a sign of a more serious hardware problem.
Using reliable antivirus software
Using reliable antivirus software is crucial to protect your computer from malware, viruses, and other online threats. Here’s a guide to help you choose and use the right antivirus software:
Choosing a Reliable Antivirus Software
When selecting antivirus software, consider the following factors:
- Reputation and Reviews: Look for software with a strong reputation and positive reviews from reputable sources.
- Features: Choose software that offers essential features like real-time protection, malware scanning, firewall, and phishing protection.
- Compatibility: Ensure the software is compatible with your operating system (Windows, macOS, Linux) and other installed programs.
- Performance: Look for software that doesn’t significantly impact your computer’s performance.
- Cost: Consider your budget and choose a software that fits your needs and price range.
Popular Antivirus Software Options
Here are some highly regarded antivirus software options:
- Bitdefender: Known for its excellent malware detection and minimal performance impact.
- Norton 360: Offers comprehensive protection with features like VPN, password manager, and secure backup.
- McAfee Total Protection: Provides robust security with a focus on online privacy and identity protection.
- Kaspersky Total Security: Offers advanced protection against malware, ransomware, and online threats.
- Avast One: A free antivirus option with essential features and good protection.
Using Antivirus Software Effectively
To get the most out of your antivirus software, follow these best practices:
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update your antivirus software to ensure it has the latest virus definitions and security patches.
- Scan Regularly: Perform full system scans at least once a week to detect and remove any hidden malware.
- Be Cautious with Downloads: Only download files from trusted sources and avoid clicking on suspicious links or attachments.
- Use Strong Passwords: Create strong, unique passwords for all your online accounts to prevent unauthorized access.
- Enable Real-Time Protection: Keep real-time protection enabled to monitor your system for potential threats.
- Be Wary of Phishing Attempts: Be cautious of emails or messages that ask for personal information or request you to click on suspicious links.

While the Blue Screen of Death can be frustrating, understanding its causes and following effective troubleshooting steps can help you resolve the issue and prevent future occurrences. By addressing hardware problems, updating drivers, scanning for malware, and checking system file integrity, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of encountering BSODs in Windows 11.